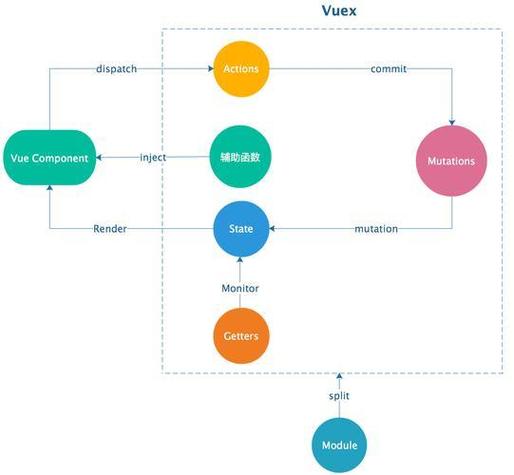
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式和库,它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化,Vuex 的核心思想是将共享状态抽取出来,形成一个全局唯一的数据源,让组件树中的任何组件都能以可预测的方式访问和修改这个状态,以下是 Vuex 的详细使用方法。
需要在项目中安装 Vuex,可以通过 npm 或 yarn 进行安装,命令分别为 npm install vuex@next 或 yarn add vuex@next,安装完成后,在项目的入口文件 main.js 中引入 Vuex 并创建 store 实例。
import { createStore } from 'vuex';
import App from './App.vue';
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
count: 0,
user: null
};
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
},
setUser(state, payload) {
state.user = payload;
}
},
actions: {
async fetchUser({ commit }) {
const response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/user');
const user = await response.json();
commit('setUser', user);
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2;
},
isLoggedIn(state) {
return state.user !== null;
}
}
});
new App({
render() {
return h(App, { store });
},
setup() {
provide('store', store);
}
}).$mount('#app');
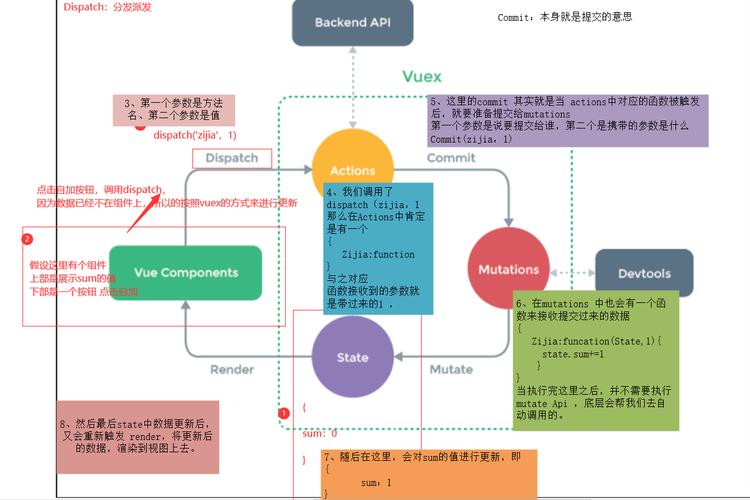
在上述代码中,state 是 Vuex 存储的核心,用于存储应用的状态。mutations 是唯一可以修改 state 的地方,必须是同步函数。actions 用于处理异步操作,通过提交 mutations 来修改状态。getters 类似于 Vue 的计算属性,用于从 state 中派生出一些状态。
在组件中使用 Vuex 时,可以通过 mapState、mapMutations、mapActions 和 mapGetters 辅助函数简化代码。
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetters(['doubleCount', 'isLoggedIn'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['increment']),
...mapActions(['fetchUser'])
},
created() {
this.fetchUser();
}
};
还可以通过 this.$store 直接访问 store 实例,this.$store.state.count 或 this.$store.commit('increment'),但为了代码的可维护性,推荐使用辅助函数。
Vuex 还支持模块化,将 store 分割成模块,每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutations、actions 和 getters。
const userModule = {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
profile: null
}),
mutations: {
setProfile(state, payload) {
state.profile = payload;
}
},
actions: {
async fetchProfile({ commit }) {
const response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/profile');
const profile = await response.json();
commit('setProfile', profile);
}
}
};
const store = createStore({
modules: {
user: userModule
}
});
在模块化 store 中,访问 state 和调用 mutations/actions 时需要指定模块名,this.$store.state.user.profile 或 this.$store.commit('user/setProfile', profile),使用 namespaced: true 可以开启命名空间,避免不同模块之间的命名冲突。
为了更好地理解 Vuex 的使用,以下是一个简单的表格,展示了 Vuex 的核心概念及其作用:
| 概念 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| state | 存储应用的状态,是唯一的数据源 |
| mutations | 修改 state 的唯一途径,必须是同步函数 |
| actions | 处理异步操作,通过提交 mutations 修改状态 |
| getters | 从 state 中派生出状态,类似于计算属性 |
| modules | 将 store 分割成模块,每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutations、actions 和 getters |
在实际开发中,需要注意以下几点:一是 mutations 必须是同步函数,因为 devtool 工具需要捕捉到状态的变化;二是 actions 可以包含任意异步操作,但不能直接修改 state,必须通过提交 mutations;三是合理使用模块化,避免 store 过于臃肿;四是避免在组件中直接修改 state,而是通过 mutations 或 actions 进行修改。
相关问答FAQs:
-
问:Vuex 和 Pinia 有什么区别? 答:Vuex 是 Vue 2 的官方状态管理库,而 Pinia 是 Vue 3 的官方推荐状态管理库,Pinia 相比 Vuex 更加轻量级,提供了更好的 TypeScript 支持,取消了 mutations,直接使用 actions 修改 state,并且支持模块化和命名空间,但语法更加简洁,Pinia 的 API 设计更加直观,不需要嵌套模块,适合中大型项目。
-
问:什么时候应该使用 Vuex? 答:Vuex 适用于中大型 Vue 应用,尤其是当多个组件需要共享状态时,用户登录状态、购物车数据、全局配置等,如果应用规模较小,组件之间的状态可以通过 props 和 events 进行管理,此时使用 Vuex 可能会增加复杂度,对于 Vue 3 项目,推荐使用 Pinia,因为它更符合 Vue 3 的设计理念,并且提供了更好的开发体验。