在Web开发中,搜索框是用户交互的核心组件之一,JavaScript(JS)是实现搜索功能的关键技术,通过JS,可以实现实时搜索、动态过滤、异步请求等高级功能,提升用户体验,本文将详细介绍如何使用JS构建一个功能完善的搜索框,包括基础实现、优化技巧和进阶功能。

基础搜索框实现
HTML结构
首先需要构建搜索框的基本HTML结构,通常包含输入框和搜索按钮。
<input type="text" id="searchInput" placeholder="请输入搜索内容..."> <button id="searchButton">搜索</button> <div id="searchResults"></div>
CSS样式
通过CSS美化搜索框,提升视觉效果,可以设置输入框的宽度、边框、圆角等属性,
#searchInput {
width: 300px;
padding: 8px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
#searchButton {
padding: 8px 16px;
background-color: #007bff;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
}
JS基础交互
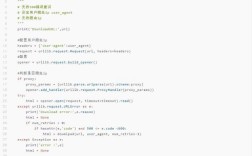
使用JS监听输入框和按钮的点击事件,实现简单的搜索功能。
document.getElementById('searchButton').addEventListener('click', function() {
const searchTerm = document.getElementById('searchInput').value;
if (searchTerm.trim() !== '') {
alert('搜索内容:' + searchTerm);
}
});
实时搜索与动态过滤
防抖(Debounce)技术
实时搜索需要在用户输入时频繁触发请求,但频繁请求可能导致性能问题,通过防抖技术,可以延迟执行搜索函数,
function debounce(func, delay) {
let timeoutId;
return function() {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
timeoutId = setTimeout(func, delay);
};
}
function performSearch() {
const searchTerm = document.getElementById('searchInput').value;
// 搜索逻辑
}
document.getElementById('searchInput').addEventListener('input', debounce(performSearch, 300));
动态过滤本地数据
如果搜索数据存储在本地,可以通过JS动态过滤并显示结果。
const data = ['苹果', '香蕉', '橙子', '葡萄'];
function performSearch() {
const searchTerm = document.getElementById('searchInput').value.toLowerCase();
const filteredData = data.filter(item => item.toLowerCase().includes(searchTerm));
displayResults(filteredData);
}
function displayResults(results) {
const resultsDiv = document.getElementById('searchResults');
resultsDiv.innerHTML = results.map(item => `<div>${item}</div>`).join('');
}
异步搜索与API集成
使用Fetch API
当搜索数据需要从服务器获取时,可以使用Fetch API发送异步请求。
async function performSearch() {
const searchTerm = document.getElementById('searchInput').value;
const response = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/search?q=${searchTerm}`);
const data = await response.json();
displayResults(data);
}
错误处理与加载状态
在异步搜索中,需要处理错误和加载状态,提升用户体验。
async function performSearch() {
const searchTerm = document.getElementById('searchInput').value;
const resultsDiv = document.getElementById('searchResults');
resultsDiv.innerHTML = '<div>加载中...</div>';
try {
const response = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/search?q=${searchTerm}`);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error('网络错误');
const data = await response.json();
displayResults(data);
} catch (error) {
resultsDiv.innerHTML = `<div>错误:${error.message}</div>`;
}
}
搜索结果优化
高亮匹配文本
在搜索结果中高亮匹配的关键词,提升可读性。
function highlightText(text, searchTerm) {
const regex = new RegExp(`(${searchTerm})`, 'gi');
return text.replace(regex, '<mark>$1</mark>');
}
function displayResults(results) {
const resultsDiv = document.getElementById('searchResults');
resultsDiv.innerHTML = results.map(item =>
`<div>${highlightText(item, searchTerm)}</div>`
).join('');
}
分页与无限滚动
当搜索结果较多时,可以实现分页或无限滚动功能。
let currentPage = 1;
const resultsPerPage = 10;
async function loadMoreResults() {
const searchTerm = document.getElementById('searchInput').value;
const response = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/search?q=${searchTerm}&page=${currentPage}`);
const data = await response.json();
displayResults(data);
currentPage++;
}
window.addEventListener('scroll', function() {
if (window.innerHeight + window.scrollY >= document.body.offsetHeight) {
loadMoreResults();
}
});
搜索框功能对比
以下是不同搜索功能的实现方式对比:
| 功能类型 | 实现方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基础搜索 | 监听点击事件 | 简单易实现 | 需要手动触发搜索 |
| 实时搜索 | 监听输入事件 + 防抖 | 即时反馈 | 可能频繁触发请求 |
| 本地数据过滤 | Array.filter() | 无需网络请求,响应快速 | 数据量大时性能较差 |
| 异步API搜索 | Fetch API + 异步处理 | 数据实时更新,支持大数据量 | 依赖网络,可能存在延迟 |
| 高亮匹配文本 | 正则表达式替换 | 提升用户体验 | 需要处理特殊字符 |
| 分页/无限滚动 | 监听滚动事件 + 分页参数 | 减少一次性加载的数据量 | 实现逻辑较复杂 |
相关问答FAQs
问题1:如何优化搜索框的性能?
解答:优化搜索框性能可以从以下几个方面入手:1)使用防抖技术减少请求频率;2)对本地数据进行缓存或索引;3)采用虚拟滚动技术处理大量数据;4)压缩API响应数据;5)使用Web Worker处理复杂计算。
问题2:搜索框如何支持中文输入法?
解答:支持中文输入法需要处理输入法的compositionstart和compositionend事件,避免在输入过程中触发搜索。
let isComposing = false;
document.getElementById('searchInput').addEventListener('compositionstart', () => {
isComposing = true;
});
document.getElementById('searchInput').addEventListener('compositionend', () => {
isComposing = false;
performSearch();
});
document.getElementById('searchInput').addEventListener('input', () => {
if (!isComposing) {
performSearch();
}
});