在Linux和Unix-like系统中,查看系统时间是日常管理和运维中常见的需求,掌握相关命令不仅能帮助管理员监控系统运行状态,还能在调试时间敏感型应用(如日志分析、定时任务)时发挥关键作用,以下是不同场景下查看系统时间的详细命令及用法,涵盖基础显示、时区调整、时间同步等实用功能。
基础时间查看命令
-
date命令
date是最常用的时间查看工具,默认显示当前系统时间、时区和日期格式。- 基本用法:
date
输出示例:
Mon Oct 23 14:30:45 CST 2023,其中CST表示中国标准时区。 - 自定义格式显示:
通过加格式符可灵活输出时间字段,常用格式符包括:%Y:四位年份(如2023)%m:两位月份(01-12)%d:两位日期(01-31)%H:24小时制小时(00-23)%M:分钟(00-59)%S:秒(00-60,60用于闰秒)%A:星期全称(如Monday)
示例:date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
输出:
2023-10-23 14:30:45。
- 基本用法:
-
timedatectl命令(systemd系统)
在使用systemd的发行版(如Ubuntu 16+、CentOS 7+)中,timedatectl提供了更全面的时间管理功能。 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- 查看时间状态:
timedatectl status
输出包含当前时间、时区、是否启用NTP同步等信息。
- 仅显示日期和时间:
timedatectl | grep "Local time"
- 查看时间状态:
硬件时间与系统时间同步
硬件时间(CMOS时间)与系统时间可能因不同步导致问题,可通过以下命令管理:
- 查看硬件时间:
hwclock
或
hwclock --show,输出示例:Mon 23 Oct 2023 02:30:45 PM CST -0.418724 seconds。 - 同步系统时间到硬件时间:
hwclock --systohc
- 同步硬件时间到系统时间:
hwclock --hctosys
时区管理
系统时区影响时间显示的准确性,需根据实际需求调整:
- 查看当前时区:
timedatectl | grep "Time zone"
- 列出所有时区:
timedatectl list-timezones
- 设置时区:
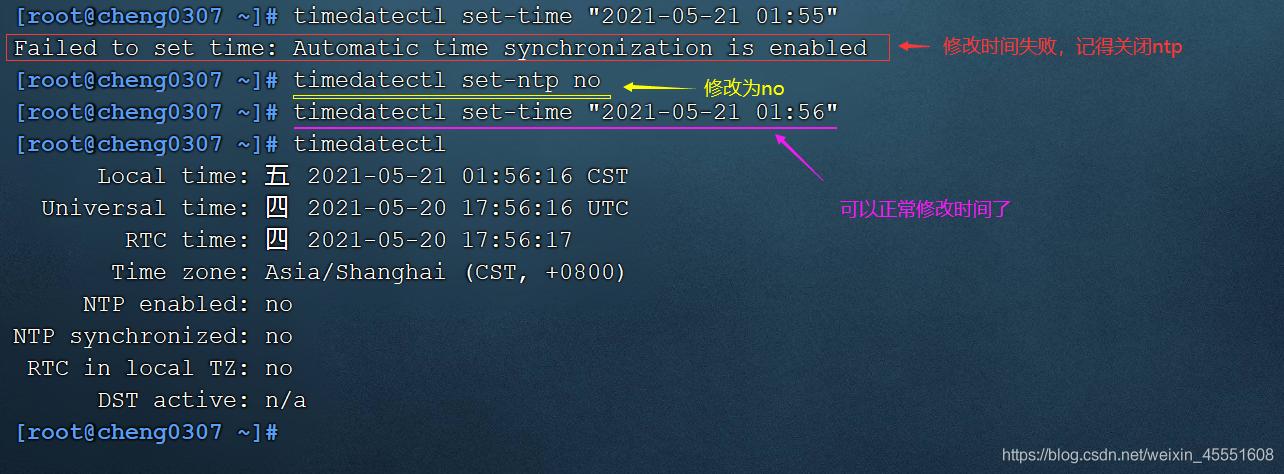
以切换为"Asia/Shanghai"为例:sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai
网络时间同步(NTP)
为避免时间漂移,通常需通过NTP服务与时间服务器同步:
- 安装NTP服务(以Ubuntu为例):
sudo apt install ntp
- 手动同步时间:
sudo ntpdate pool.ntp.org
- 启用自动同步(通过
timedatectl):sudo timedatectl set-ntp yes
不同发行版的命令差异
| 功能 | Debian/Ubuntu命令 | RHEL/CentOS命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 查看时间状态 | timedatectl status |
timedatectl status |
systemd通用 |
| 安装NTP | apt install ntp |
yum install ntp |
需root权限 |
| 手动同步时间 | ntpdate pool.ntp.org |
ntpdate pool.ntp.org |
需安装ntp工具包 |
高级时间格式化
date命令支持复杂格式化,
- 显示Unix时间戳:
date +%s
- 从时间戳转换回可读时间:
date -d @1698067245
- 显示UTC时间:
date -u
常见问题解决
- 时间显示错误:
- 检查时区设置是否正确,执行
timedatectl set-timezone调整。 - 若时间与硬件时间不符,使用
hwclock --systohc同步。
- 检查时区设置是否正确,执行
- NTP同步失败:
- 检查网络连通性:
ping pool.ntp.org。 - 确认防火墙是否允许UDP 123端口。
- 检查网络连通性:
相关问答FAQs
Q1: 如何在Linux中查看特定时区的时间?
A1: 使用date命令结合TZ环境变量即可,例如查看纽约时间:
TZ="America/New_York" date
若需持久化修改,可通过timedatectl set-timezone设置系统时区,或仅临时在脚本中使用TZ变量。
Q2: 系统时间与硬件时间不一致时,如何确定哪个是正确的?
A2: 通常系统时间(由Linux内核维护)更准确,尤其是联网服务器通过NTP同步后,硬件时间(由主板CMOS芯片存储)可能在断电后仍保留,但可能因电池老化漂移,建议优先以系统时间为准,若硬件时间明显错误(如与实际时间差几小时),可通过hwclock --systohc将系统时间写入硬件时间。