JavaScript 中正则表达式是一种强大的文本处理工具,它允许开发者通过定义模式来搜索、匹配、替换和验证字符串,正则表达式在 JavaScript 中主要通过 RegExp 对象和字符串方法来实现,掌握其使用方法对于处理复杂文本任务至关重要,本文将详细介绍 JavaScript 中正则表达式的创建、方法使用、高级特性及实际应用场景。
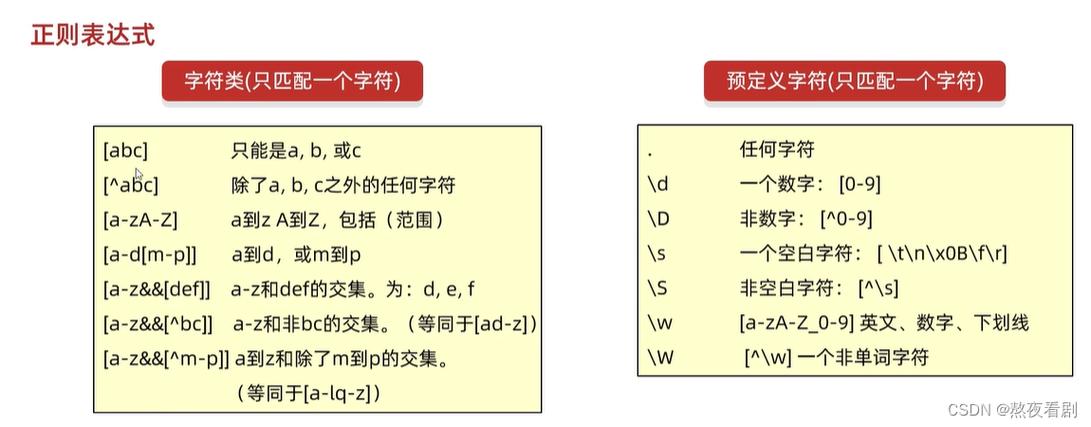
正则表达式的创建
在 JavaScript 中,正则表达式可以通过两种方式创建:字面量方式和构造函数方式。
- 字面量方式:使用斜杠 包裹模式,
/pattern/flags。const regex = /hello/g;
- 构造函数方式:通过
new RegExp(pattern, flags)创建,适用于动态构建正则表达式。const regex = new RegExp('hello', 'g');flags是修饰符,常用的有:
g:全局匹配,查找所有匹配项而非第一个。i:忽略大小写。m:多行匹配,影响^和 的行为。s:单行模式, 匹配包括换行符在内的所有字符。
正则表达式的方法
JavaScript 中,RegExp 对象和字符串都提供了与正则表达式相关的方法。
RegExp 对象的方法
exec():执行匹配操作,返回匹配数组和相关信息,若无匹配则返回null。const regex = /hello/g; const str = 'hello world, hello javascript'; console.log(regex.exec(str)); // 输出: ["hello", index: 0, input: "hello world, hello javascript", groups: undefined]
test():测试字符串是否匹配正则表达式,返回布尔值。const regex = /^[a-zA-Z]+$/; console.log(regex.test('Hello')); // true console.log(regex.test('123')); // false
字符串的方法
match():返回匹配结果的数组,若使用g修饰符则返回所有匹配项。const str = '2023-10-01'; console.log(str.match(/\d+/g)); // ["2023", "10", "01"]
matchAll():返回一个迭代器,包含所有匹配的详细信息(ES2020 新增)。const str = 'a1 b2 c3'; const matches = str.matchAll(/\d/g); for (const match of matches) { console.log(match); // 依次输出 ["1"], ["2"], ["3"] }replace():替换匹配的子字符串,支持回调函数动态替换。const str = 'hello world'; console.log(str.replace(/hello/, 'hi')); // "hi world"
search():返回第一个匹配项的索引,无匹配则返回-1。const str = 'javascript is fun'; console.log(str.search(/java/)); // 0
split():根据正则表达式分割字符串。const str = 'a,b;c|d'; console.log(str.split(/[,;|]/)); // ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
正则表达式的高级特性
分组和引用
- 分组:使用 创建子表达式,可用于限定作用域或提取匹配内容。
const regex = /(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})/; const str = '2023-10-01'; console.log(regex.exec(str)); // ["2023-10-01", "2023", "10", "01", index: 0, input: "2023-10-01", groups: undefined] - 引用:通过
$n或\n引用分组匹配的内容($n用于replace方法)。const str = 'hello world'; console.log(str.replace(/(\w+)\s(\w+)/, '$2 $1')); // "world hello"
零宽断言
零宽断言用于匹配位置而非字符,包括:

- 正向先行断言,匹配后面满足条件的字符。
const regex = /\w(?=\d)/; // 匹配数字前的字母 console.log('a1 b2'.match(regex)); // ["a", "b"] - 负向先行断言,匹配后面不满足条件的字符。
(?<=...):正向后行断言(ES2018 支持),匹配前面满足条件的字符。(?<!...):负向后行断言,匹配前面不满足条件的字符。
量词和贪婪模式
- 量词:(0次或多次)、(1次或多次)、(0次或1次)、
{n,m}(n到m次)。 - 贪婪模式:默认匹配尽可能多的字符,可通过 转为非贪婪模式。
const regex = /<.*>/; // 贪婪模式 console.log('<div>hello</div>'.match(regex)); // ["<div>hello</div>"] const regex2 = /<.*?>/; // 非贪婪模式 console.log('<div>hello</div>'.match(regex2)); // ["<div>"]
特殊字符和转义
正则表达式中的特殊字符(如 、、 等)需通过 \ 转义。
const regex = /\.html$/;
console.log(regex.test('index.html')); // true
实际应用场景
表单验证
// 验证邮箱格式
const emailRegex = /^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/;
console.log(emailRegex.test('user@example.com')); // true
提取信息
// 从URL中提取域名
const urlRegex = /https?:\/\/([^\/]+)/;
console.log(urlRegex.exec('https://www.example.com/path')[1]); // "www.example.com"
替换敏感词
const str = '这是一个敏感词测试'; console.log(str.replace(/敏感词/g, '***')); // "这是一个***测试"
性能优化建议
- 避免使用全局匹配:在循环中慎用
g修饰符,可能导致性能问题。 - 预编译正则表达式:对于频繁使用的正则表达式,使用
RegExp构造函数预编译。 - 简化复杂正则:拆分复杂正则表达式为多个简单正则,提高可读性和性能。
常见错误与调试
- 错误:未正确转义特殊字符。
修正:使用\转义或String.escapeRegExp()工具函数。 - 错误:忽略贪婪陷阱导致匹配结果不符合预期。
修正:使用 转为非贪婪模式。
相关问答FAQs
Q1: 如何在正则表达式中匹配换行符?
A: 默认情况下, 不匹配换行符,可通过 s 修饰符(ES2018)或使用 [\s\S] 匹配所有字符(包括换行符)。/hello[\s\S]world/s。
Q2: 如何实现正则表达式的动态拼接?
A: 使用 RegExp 构造函数动态拼接字符串,并注意转义特殊字符。
const dynamicPart = 'user@';
const regex = new RegExp(`^${dynamicPart}[^\s@]+$`);
console.log(regex.test('user@example.com')); // true